Suffering from back ache and neck pain?
Is surgery or operation is the only
solution for your back pain?
What if the surgery is not
successful and you become paralysed?
Let us help You!
We have answer for all your questions!!!
Introduction
What are the risk factors for back pain?
· A mentally stressful job
· Pregnancy - pregnant women are much more likely to get back pain
· A sedentary lifestyle
· Age - older adults are more susceptible than young adults or children
· Anxiety
· Depression
· Gender - back pain is more common among females than males
· Obesity/overweight
· Smoking
.jpg)
What are the causes of back pain?
Your back is a complex structure that provides support for your pelvis, legs, ribcage, arms and skull. The spine is made up of bones called vertebrae that are stacked together to form a loose ‘S’-shaped column.
Each vertebra is cushioned by spongy tissue or cartilage called intervertebral discs. The discs have a flat structure with a jelly-like centre. Vertebrae are joined by pairs of small joints known as ‘facet’ joints. A mesh of connective tissue called ligaments holds the spine together.
Complex layers of muscle provide structural support and allow movement. The spinal cord runs through the centre of the vertebral stack and connects the brain to the rest of the body.
Problems with any of these components can lead to back pain. In some cases of back pain, its cause is never found.
Strain - the most common causes of back pain are:
· Strained muscles
· Strained ligaments
· Lifting something improperly
· The result of an abrupt and awkward movement
· A muscle spasm
· Ruptured disks - each vertebra in our spine is cushioned by disks. If the disk ruptures there will be more pressure on a nerve, resulting in back pain.

.jpg)
· Bulging disks - in much the same way as ruptured disks, a bulging disk can result in more pressure on a nerve.
· Sciatica - a sharp and shooting pain that travels through the buttock and down the back of the leg, caused by a bulging or herniated disk pressing on a nerve.
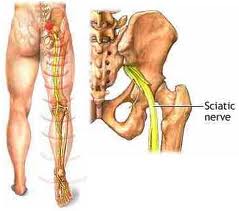.jpg)
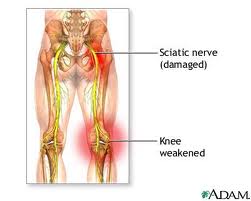.jpg)
· Arthritis - patients with osteoarthritis commonly experience problems with the joints in the hips, lower back, knees and hands. In some cases spinal stenosis can develop - the space around the spinal cord narrows.
· Abnormal curvature of the spine - if the spine curves in an unusual way the patient is more likely to experience back pain. An example is scoliosis, when the spine curves to the side.
· Osteoporosis - bones, including the vertebrae of the spine, become brittle and porous, making compression fractures more likely.
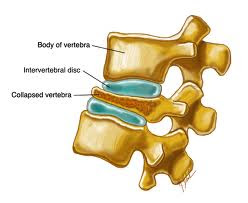.jpg)
Below are some other causes of back pain:
· Cauda equina syndrome - the cauda equine is a bundle of spinal nerve roots that arise from the lower end of the spinal cord. People with cauda equine syndrome feel a dull pain in the lower back and upper buttocks, as well as analgesia (lack of feeling) in the buttocks, genitalia and thigh. There are sometimes bowel and bladder function disturbances.
· Cancer of the spine - a tumor located on the spine may press against a nerve, resulting in back pain.
· Infection of the spine - if the patient has an elevated body temperature (fever) as well as a tender warm area on the back, it could be caused by an infection of the spine.
· Other infections - pelvic inflammatory disease (females), bladder or kidney infections.
· Sleep disorders - individuals with sleep disorders are more likely to experience back pain, compared to others.
· Shingles - an infection that can affect the nerves.
· Bad mattress - if a mattress does not support specific parts of the body and keep the spine straight, there is a greater risk of developing back pain.
.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)






